How Long Until a Tooth Infection Kills You: Understanding the Stages and Risks
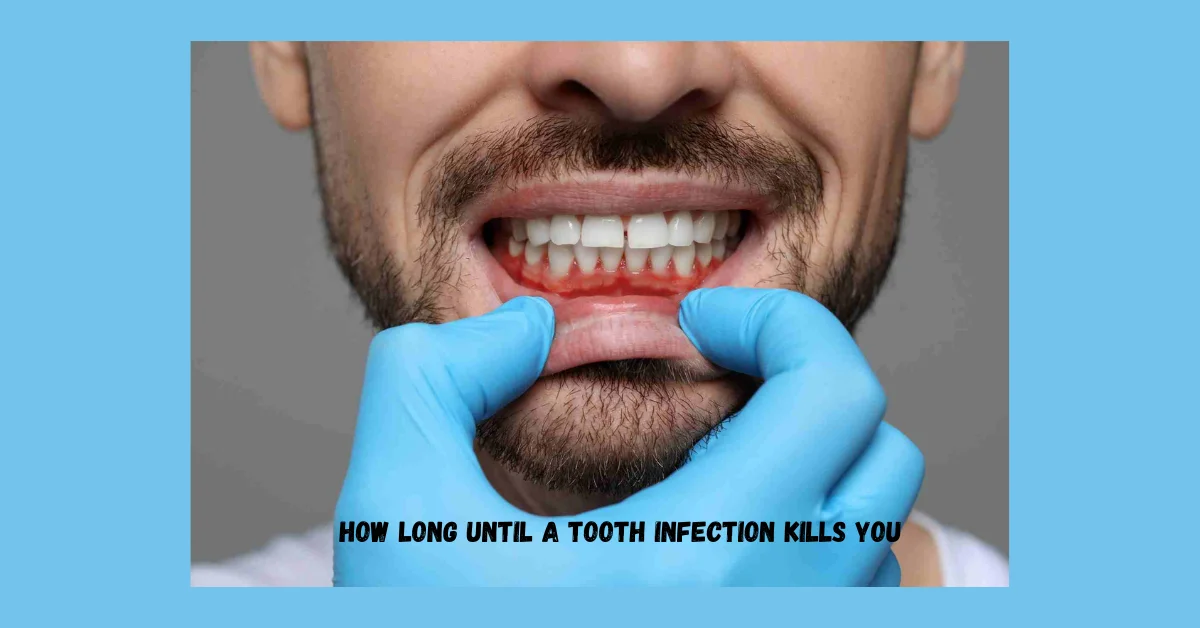
There’s no specific timeframe for how long until a tooth infection kills you. Think about it in terms of stages. The sooner you get a tooth infection treated, the earlier you can return to your healthy and happy life. If a tooth infection is left untreated, it can take several weeks or months to develop an abscess. This is because the decay process is gradual, and it usually takes a while to reach and infect the pulp at a tooth’s center. Once it has reached the center of a tooth, you can still save your natural tooth by undergoing a root canal treatment. However, if your tooth is infected due to an injury or a trauma, the bacteria will reach the pulp more quickly.
Can a Tooth Abscess Kill You?
If you are wondering how long until a tooth infection kills you, you first need to understand how the infection develops and then spreads to other areas of the body. If bacteria penetrate into your tooth and reaches the soft tissue area located in the center of the tooth (known as pulp), then an infection will usually develop. Over time, this infection can continue to progress, resulting in an abscess that can form around the infected tooth. This abscess is a pocket of infection and pus, and it will continue to worsen and can cause severe symptoms, including pain, toothache, and more.
Signs and Symptoms of Dental Infections
Dental infections can manifest in various ways, and it’s important to be aware of the signs and symptoms. One of the most common symptoms is persistent tooth pain, which may worsen when biting or chewing. You may also notice swelling and tenderness in the gums around the affected tooth, along with a foul taste or odor in your mouth. In some cases, dental infections can cause systemic symptoms, such as fever, headache, and swollen lymph nodes. These symptoms indicate that the infection has spread beyond the tooth and may require immediate medical attention. It’s essential to pay attention to these signs and symptoms and seek prompt dental care if you suspect a dental infection.
When is a Tooth Infection an Emergency?
A tooth infection turns into an emergency when specific symptoms appear. It’s critical if you have excruciating pain, swelling, or trouble breathing. A high fever or a bad taste may also be signs of a serious problem. These signs imply that the infection can spread quickly and call for quick treatment. In these situations, get emergency dental care right away to avoid developing more issues. By being aware of these symptoms, you may take prompt action to improve the state of your dental health by recognizing when a tooth infection calls for it.
Read Previous: https ://clicpagado. blogspot.com/2024/04/coca-cola.html
Treatment Options and Preventing Tooth Infections
Fortunately, tooth infections are treatable, especially when caught early. The key is recognizing the symptoms and seeking prompt dental care to prevent complications. Below are the most common treatment options for tooth infections:
- Antibiotics: Dentists typically prescribe antibiotics to stop the infection from spreading. While antibiotics can help reduce the infection and alleviate symptoms, they are not a permanent solution. The root cause of the infection must still be addressed.
- Root Canal Therapy: This procedure is used to save an infected tooth. During a root canal, the dentist removes the infected pulp from inside the tooth, cleans the root canals, and seals the tooth to prevent further infection. Root canals are highly effective in stopping the infection and saving the tooth.
- Tooth Extraction: In severe cases where the tooth cannot be saved, extraction may be necessary. Removing the infected tooth eliminates the source of the infection and prevents it from spreading further.
- Drainage of Abscess: In some cases, a dentist may need to drain the abscess to relieve pressure and remove the buildup of pus. This is often combined with other treatments like antibiotics.
How Do You Know If a Tooth Infection Has Spread to Your Blood?
If the infection spreads to your blood, then it is known as sepsis. This severe infection can be quite serious and is one of the potential causes of death from a tooth infection. But rest assured knowing that sepsis after a bacterial infection is rare. If it occurs, then it could be life-threatening if the medical treatments aren’t administered correctly. What are the chances of getting sepsis from a tooth infection? The risk is very low if you treat a tooth infection in the earliest stages. The longer a tooth infection goes untreated, the higher the risk of sepsis. So, early detection and treatment is key to preventing this serious systemic infection.
Is Death from a Tooth Infection Rare?
While death from a tooth infection is not an everyday occurrence, it is not as rare as one might hope. As mentioned earlier, the mortality rate associated with severe dental infections is around 0.4%. While this percentage may seem relatively low, it emphasizes the importance of prompt and appropriate treatment. Moreover, it is crucial to understand that the risks associated with tooth infections extend beyond mortality. Even when death is not the outcome, untreated or improperly managed infections can lead to significant pain, loss of teeth, and the need for more invasive and complex dental treatments. Tooth infections can also have a significant impact on an individual’s overall health. Studies have suggested potential links between oral infections and systemic conditions such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and respiratory infections.
Can Antibiotics Cure a Tooth Infection?
Antibiotics play a pivotal role in managing tooth infections by eradicating the bacteria responsible, alleviating symptoms, and preventing systemic spread. However, their limitations lie in addressing only surface issues, not resolving underlying causes like abscesses. Dental intervention, such as drainage or root canal therapy, is often indispensable for complete resolution. Overuse risks antibiotic resistance. Adhering to prescribed courses, coupled with timely dental care, ensures a balanced approach for effective management and curbing potential complications associated with untreated dental infections.
FAQs
Can a tooth infection go away on its own?
No, a tooth infection will not go away without treatment. Infections in the tooth or gum tissue typically need professional care, as they can worsen or spread to other areas of the body if left untreated.
What are the first signs of a tooth infection?
Early signs include persistent tooth pain, sensitivity, swelling in the gums around the affected area, and sometimes a foul taste or odor in the mouth. If you experience these symptoms, it’s best to consult a dentist promptly.
Can a tooth infection spread to other parts of the body?
Yes, an untreated infection can spread to the jaw, neck, or even the bloodstream, leading to a serious condition known as sepsis. Symptoms like high fever, difficulty breathing, or swelling beyond the immediate area of the tooth can indicate that the infection is spreading and requires emergency care.
Is it safe to rely only on antibiotics for a tooth infection?
Antibiotics can help control the spread of infection temporarily, but they don’t address the root cause. Dental procedures like root canal therapy or extraction are typically required to fully resolve the infection.
Conclusion
Tooth infections are serious dental issues that require prompt attention to prevent complications. While antibiotics can help control the infection temporarily, they aren’t a long-term solution and won’t address the underlying problem. Treatments such as root canal therapy or, in severe cases, tooth extraction are often necessary to fully eliminate the infection and prevent it from spreading.
Read Next: Aurora Juarez De Huerta En California USA